The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time
Related Articles: The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time
- 3.1 Understanding the Aymaran Calendar: A Framework of Cycles
- 3.2 Beyond Time: The Aymaran Calendar and Andean Culture
- 3.3 Exploring the Months of the Aymaran Calendar:
- 3.4 The Aymaran Calendar: A Living Tradition
- 3.5 Understanding the Aymaran Calendar: FAQs
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding and Appreciating the Aymaran Calendar:
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Aymaran Calendar
- 4 Closure
The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time

The Aymaran calendar, a system of timekeeping deeply intertwined with the Andean worldview, offers a unique perspective on the relationship between humans and nature. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which is based on solar cycles, the Aymaran calendar incorporates both solar and lunar cycles, creating a complex and nuanced system that reflects the rhythms of the Andean environment.
Understanding the Aymaran Calendar: A Framework of Cycles
The Aymaran calendar is not simply a method of marking days and months; it is a framework for understanding the cyclical nature of life, the universe, and everything in between. It is a system that aligns with the movements of the sun, moon, and stars, reflecting the profound connection that Andean cultures have with the natural world.
The Core Elements:
- The Year: The Aymaran year is divided into 12 lunar months, each marked by a specific phase of the moon. These months are further divided into weeks, with each week consisting of seven days.
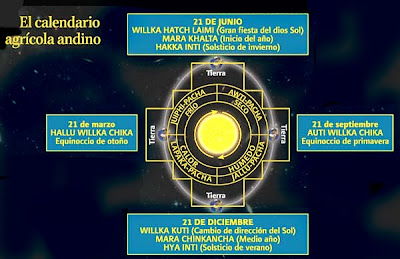
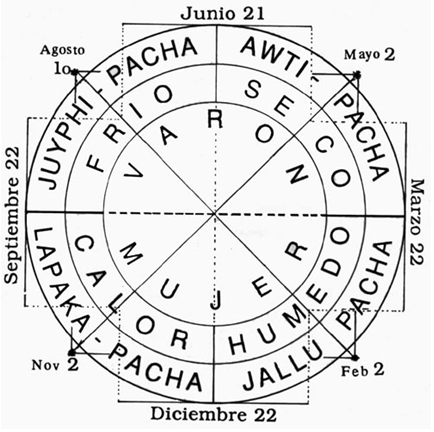
- The Solar Cycle: The Aymaran year also incorporates the solar cycle, with the solstices and equinoxes holding significant cultural and spiritual importance. These celestial events mark the turning points of the year, influencing agricultural practices and social life.
- The Pachamama: The Andean concept of Pachamama, the Earth Mother, is central to the Aymaran calendar. The calendar acknowledges the Earth’s role as a provider and a force of life, recognizing the interconnectedness of humans and the natural world.
Beyond Time: The Aymaran Calendar and Andean Culture
The Aymaran calendar is not merely a tool for tracking time; it is a cultural expression of the Andean worldview. It reflects the deep reverence for nature, the interconnectedness of all things, and the cyclical nature of life. The calendar serves as a guide for agricultural practices, social ceremonies, and spiritual observances.
A Deeper Dive into the Cultural Significance:
- Agricultural Practices: The Aymaran calendar dictates the timing of planting, harvesting, and other agricultural activities. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring successful harvests and sustaining the community.
- Social Ceremonies: Important social events, such as festivals and rituals, are aligned with the calendar, reflecting the cyclical nature of life and the importance of community.
- Spiritual Observances: The Aymaran calendar is deeply intertwined with Andean spirituality, marking key moments for prayer, offerings, and connection with the divine.
Exploring the Months of the Aymaran Calendar:
The Aymaran calendar, with its unique system of lunar months, offers a fascinating insight into the Andean worldview. Here’s a closer look at each month:
- Janu: This month, characterized by the rising of the new moon, marks the beginning of the Aymaran year. It is a time for renewal, hope, and preparation for the upcoming agricultural cycle.
- Phaxsi: The second month, known for its waning moon, is a time for reflection and planning. It is a period for assessing the previous year and preparing for the upcoming challenges.
- Lluq’i: This month, with its new moon, symbolizes the start of the rainy season in the Andes. It is a time for planting and nurturing the Earth, as the rains bring life to the land.
- Ayarachi: The fourth month, with its waning moon, is a time for tending to crops and observing the growth of the plants. It is a period of anticipation and hope for a bountiful harvest.
- Qhapaq Raymi: This month, marked by the new moon, is a time for celebrating the arrival of the sun’s strength. It is a time for festivals, music, and community gatherings.
- Anta Sitwa: The sixth month, with its waning moon, is a time for harvesting and celebrating the abundance of the Earth. It is a period for gratitude and sharing with the community.
- Pauqar Waray: This month, with its new moon, marks the beginning of the dry season. It is a time for preparing for the upcoming challenges and ensuring the preservation of resources.
- Aymuray: The eighth month, with its waning moon, is a time for reflecting on the past year and planning for the future. It is a period for community gatherings and spiritual observances.
- Simi: This month, with its new moon, symbolizes the return of the rains and the renewal of life. It is a time for planting and nurturing the Earth, as the rains bring life to the land.
- Qhapaq Yupanqui: The tenth month, with its waning moon, is a time for tending to crops and observing the growth of the plants. It is a period of anticipation and hope for a bountiful harvest.
- Hatun Puquy: This month, marked by the new moon, is a time for celebrating the arrival of the sun’s strength. It is a time for festivals, music, and community gatherings.
- Pachakutiq: The twelfth month, with its waning moon, is a time for harvesting and celebrating the abundance of the Earth. It is a period for gratitude and sharing with the community.
The Aymaran Calendar: A Living Tradition
The Aymaran calendar is not a relic of the past; it is a living tradition that continues to guide the lives of Andean communities. It is a system that embodies the wisdom of generations, reflecting the deep connection between humans and nature.
The Importance of Preservation:
- Cultural Heritage: The Aymaran calendar is an invaluable part of Andean cultural heritage, offering a unique perspective on the world and the relationship between humans and the natural environment.
- Sustainability: The calendar’s emphasis on the cyclical nature of life and the importance of sustainability aligns with modern concerns about climate change and environmental stewardship.
- Community Building: The calendar plays a vital role in strengthening community bonds, fostering shared traditions, and promoting cultural unity.
Understanding the Aymaran Calendar: FAQs
Q: What are the key differences between the Gregorian calendar and the Aymaran calendar?
A: The Gregorian calendar is based on the solar cycle, with 12 months of varying lengths. The Aymaran calendar incorporates both solar and lunar cycles, with 12 lunar months, each marked by a specific phase of the moon. The Gregorian calendar is a global system, while the Aymaran calendar is specific to Andean cultures.
Q: How does the Aymaran calendar influence agricultural practices?
A: The Aymaran calendar dictates the timing of planting, harvesting, and other agricultural activities. It provides guidance on when to sow seeds, when to expect rain, and when to harvest crops, ensuring successful harvests and the sustainability of Andean communities.
Q: What are some of the key cultural events and celebrations associated with the Aymaran calendar?
A: The Aymaran calendar is rich with cultural events and celebrations, including festivals, rituals, and ceremonies. These events mark key moments in the agricultural cycle, the solstices, and equinoxes, reflecting the deep connection between humans and nature.
Q: How is the Aymaran calendar relevant in the modern world?
A: The Aymaran calendar offers valuable insights into the cyclical nature of life, the importance of sustainability, and the interconnectedness of humans and nature. It is a reminder of the wisdom of ancient cultures and the importance of respecting the environment.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating the Aymaran Calendar:
- Learn about the history and cultural context of the calendar. Understanding the origins and significance of the Aymaran calendar is crucial for appreciating its value and relevance.
- Explore the relationship between the calendar and Andean cosmology. The Aymaran calendar is deeply intertwined with the Andean worldview, reflecting their beliefs about the universe, the Earth, and the relationship between humans and nature.
- Engage with Andean communities and learn from their knowledge and perspectives. The Aymaran calendar is a living tradition that is still practiced by Andean communities. Engaging with them offers a unique opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of the calendar and its significance.
- Connect the calendar to your own life and experiences. The Aymaran calendar offers a framework for understanding the cyclical nature of life and the interconnectedness of all things. Reflect on how these concepts resonate with your own experiences and perspectives.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Aymaran Calendar
The Aymaran calendar stands as a testament to the wisdom and resilience of Andean cultures. It is a system that reflects the deep connection between humans and nature, the cyclical nature of life, and the importance of community. The calendar continues to inspire and guide Andean communities, offering a unique perspective on time, nature, and the human experience.
As we navigate the complexities of the modern world, the Aymaran calendar serves as a reminder of the importance of respecting the natural world, celebrating cultural heritage, and fostering sustainable practices for the future. It is a system that transcends time, offering valuable insights into the interconnectedness of all things and the enduring legacy of Andean wisdom.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Aymaran Calendar: A Window into Andean Time. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!